Challenges and Opportunities in Cashless Payment in Japan: Navigating the Digital Revolution 2025
Japan has long been known for its strong cultural attachment to cash. However, over the past few years, a significant transformation has taken place in the country’s financial landscape. The rise of cashless payment in Japan is reshaping how transactions are made, driven by a combination of technological advancements, changing consumer behavior, and government initiatives. As Japan moves toward a future where cashless payments dominate, the financial industry, retail businesses, and consumers are all experiencing a shift in how they interact with money.
Current Trends and Adoption of Cashless Payment in Japan
Despite Japan’s reputation for being a cash-driven society, the trend toward digital payment methods has been gaining momentum in recent years. With the increasing adoption of mobile wallets, QR code-based payment systems, and contactless cards, cashless payment in Japan is no longer a distant dream but a growing reality. The Japanese government has also been at the forefront of this transition, encouraging cashless payments with initiatives such as the 2020 “Cashless Payment Promotion Campaign,” which offered discounts and rewards to consumers who used digital payment options.
Mobile payment platforms like PayPay, Line Pay, and Rakuten Pay have seen a surge in popularity, particularly in urban areas. These apps allow consumers to make payments easily and securely using their smartphones, QR codes, or even facial recognition. Retailers, from small shops to large corporations, have rapidly adopted these systems, leading to an expansion of digital payment infrastructure throughout the country.
Government’s Role in Promoting Cashless Payments
The Japanese government has set ambitious targets to increase the share of cashless transactions in the country. With a goal to achieve 40% of all payments being cashless by 2025, it is clear that the government is committed to transforming Japan’s payment landscape. This shift is intended to improve the overall efficiency of the economy, reduce transaction costs, and offer greater convenience for both consumers and businesses.
In addition to promotional campaigns, Japan’s government is also investing in the infrastructure necessary to support cashless transactions. Public transportation systems, vending machines, and retail outlets are increasingly equipped with digital payment terminals, providing a seamless experience for consumers who prefer to use their smartphones or contactless cards.
Technological Advancements Driving the Shift
Several technological innovations have played a crucial role in making cashless payment in Japan more accessible and secure. For instance, near-field communication (NFC) technology, which allows for tap-and-go payments, has become widely integrated into smartphones, credit cards, and public transport systems. With just a simple tap, consumers can complete their transactions, eliminating the need for physical cash.
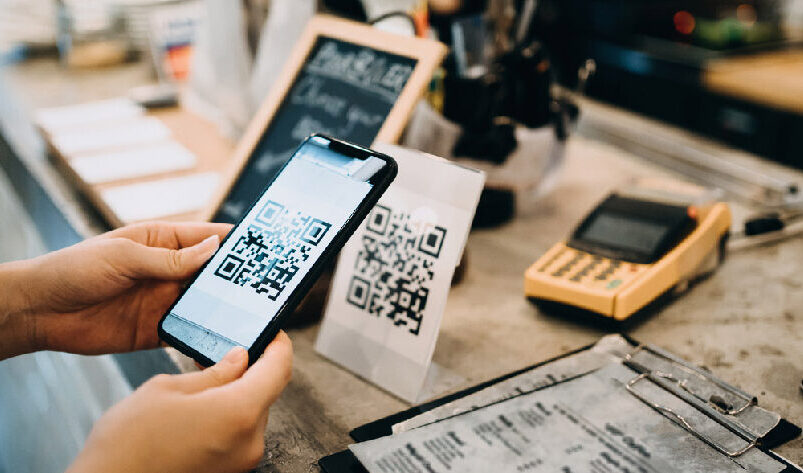
QR code-based payment systems have also gained popularity in Japan, particularly in small businesses and convenience stores. These systems are easy to implement and enable instant payment processing. Consumers simply scan a merchant’s QR code using their mobile app, and the transaction is completed without the need for any physical exchange of money.
Moreover, advancements in biometric technologies, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, are making transactions even more secure and convenient. These technologies help to eliminate concerns about fraud or theft, which can be associated with traditional payment methods. As biometric authentication becomes more commonplace, it is expected to further encourage the adoption of cashless payment in Japan.
The Role of Cashless Payments in the Post-Pandemic World
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on payment habits around the world, and Japan is no exception. With health concerns and social distancing guidelines in place, consumers have increasingly turned to cashless payment methods to reduce physical contact and minimize the risk of transmission. The convenience and hygiene of mobile payments and contactless transactions have made them an attractive alternative to handling physical currency.
For many businesses, the shift toward cashless payments has also been a way to ensure continuity during periods of restricted in-person interactions. The pandemic has accelerated digital adoption across various sectors, including retail, hospitality, and transportation, pushing Japan further toward a cashless society.
Challenges to Widespread Cashless Payment Adoption
While cashless payment in Japan is steadily growing, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed in order to achieve widespread adoption. One of the biggest hurdles is Japan’s aging population. Many elderly individuals in Japan are not as familiar with digital payment methods and still prefer using cash for daily transactions. Although younger generations are increasingly embracing mobile payments, older consumers may require additional support and education to transition to digital systems.
Another challenge is cybersecurity. As cashless transactions become more prevalent, the risks associated with data breaches and fraud increase. Consumers need to feel confident that their personal and financial information is protected when using mobile wallets and other digital payment systems. Payment service providers and the government must continue to prioritize security and ensure that measures are in place to protect against cybercrime.
Additionally, the infrastructure for cashless payments is still uneven across Japan. While urban areas such as Tokyo and Osaka are well-equipped with the necessary payment terminals, rural areas face challenges in terms of internet access, digital literacy, and merchant adoption. The government and private companies must collaborate to ensure that digital payment systems are accessible to all, regardless of location or technological familiarity.
The Future of Cashless Payments in Japan
Looking ahead, cashless payment in Japan is expected to evolve rapidly. The introduction of new technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) will likely revolutionize how payments are processed and secured. Blockchain, for example, has the potential to provide decentralized, transparent, and highly secure payment systems that could replace traditional banking methods. Similarly, AI-powered tools can enhance fraud detection and improve the overall user experience by offering personalized payment solutions.
Another exciting possibility is the development of a central bank digital currency (CBDC) in Japan. The Bank of Japan has already begun experimenting with the idea of a digital yen, which could offer faster, more efficient, and secure transactions while reducing reliance on traditional banking systems. If implemented, the digital yen could become a core part of Japan’s future payment infrastructure, further solidifying the country’s move toward a cashless economy.
In the coming years, Japan is also expected to see greater integration of cashless payment in Japan with other global payment systems. As international visitors return post-pandemic, the ability to use global payment platforms seamlessly in Japan will become increasingly important. This could lead to greater interoperability between Japan’s domestic payment systems and global networks like Visa, Mastercard, and Alipay.
Conclusion
The future of cashless payment in Japan is bright and promising. While there are challenges to overcome, such as an aging population and infrastructure gaps, the overall trend is moving toward greater adoption of digital payments. With government support, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences, Japan is well on its way to becoming a leader in the global shift toward a cashless society. As this transition unfolds, Japan’s financial landscape will continue to be reshaped, offering new opportunities for businesses, consumers, and financial institutions alike.